Last month, RSI reached the end of an 18-month grant from the American Arbitration Association-International Centre for Dispute Resolution (AAA-ICDR) Foundation. A primary goal of the grant was to provide guidance to courts nationwide about addressing the eviction crisis arising from the COVID-19 pandemic. As that project has come to a close, we at RSI would like to look back at what we accomplished, and learned, from the experience.
Our Eviction Mediation Program and Special Topic
The first focus of the grant was to help us establish a local court mediation program, serving Kane County, Illinois. While it may seem counterintuitive that a project with a focus on national guidance invest in a local program, our approach at RSI is to utilize our mediation programs as “laboratories” for the research and evaluation that is core to our mission. We have a long history of designing and administering programs, and as part of that work, we implement established best practices, set up robust monitoring and evaluation systems, and carefully and thoughtfully test out different approaches to help us achieve the goals we set for our programs. The Kane County Eviction Mediation program is no exception (See related article above), and it served as the basis for many exciting accomplishments of the project, detailed further below.

Our next big milestone was developing the Eviction Mediation Special Topic. Special Topics are collections of resources RSI curates around court alternative dispute resolution (ADR) as it relates to different subject matter (e.g., child protection mediation and restorative justice) or interested parties (e.g., judges and lawyers). For eviction, we sought to develop a Special Topic collection that was both topical to the present crisis and also highlighted the best research, guidance and tools for those invested in the development and administration of effective eviction diversion programs.
Blogs and Evaluation Projects
Throughout the 18 months of the grant, the RSI team was regularly blogging about our experiences developing and administering our programs, and what we were learning from others across the country. A few highlights from our blogging include glimpses into innovative program models in Hawaii and Philadelphia, and program design considerations such as working with rental assistance programs and cultivating buy-in from landlords. Additionally, a pair of Q&As with our Programs Manager Chris Riehlmann and our Kane County Program Coordinator Christina Wright provide a great look into what it really takes to make these program work day in and day out.
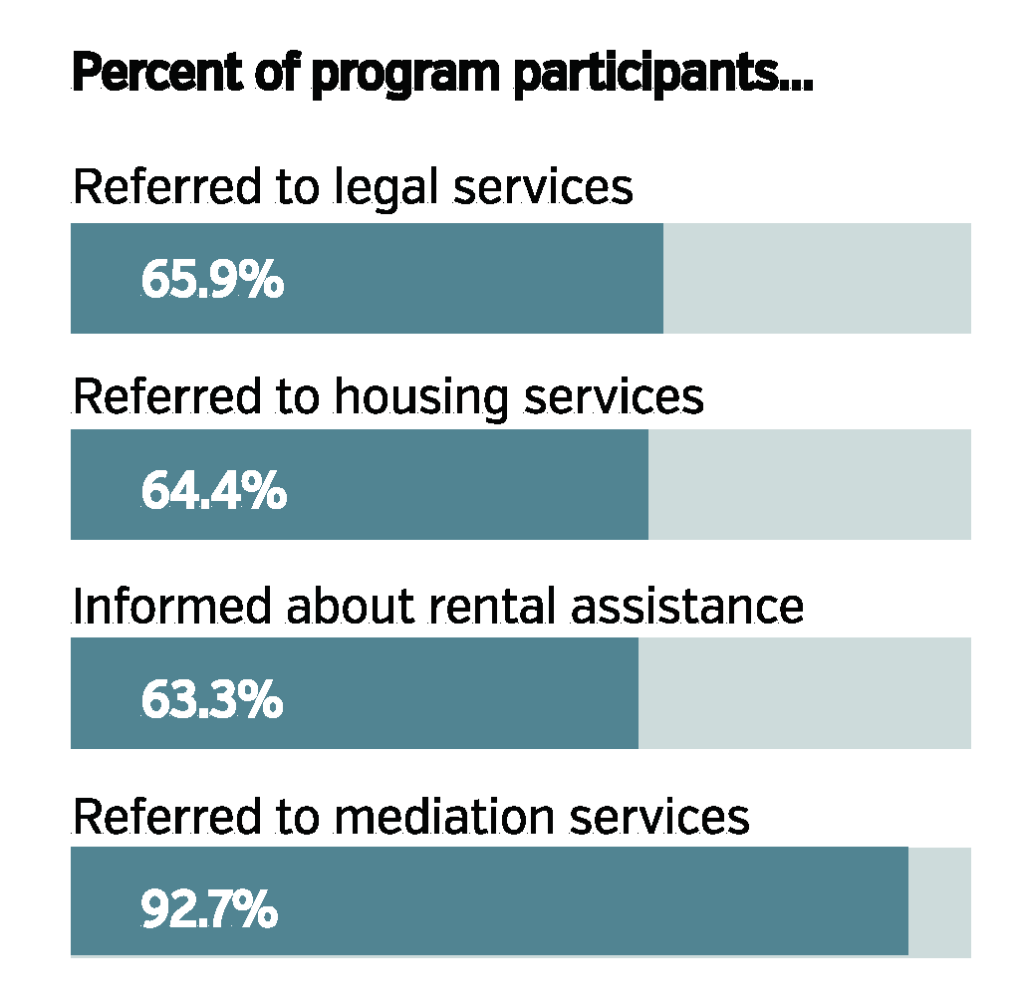
Finally, and most significantly, the grant supported several evaluative projects we embarked on over this past year and a half. We analyzed the results of our post-mediation surveys to assess whether our programs were providing procedural justice to participants. After reflecting on the steps we’d taken to develop programs and conducting interviews with key program personnel and partners, RSI published program implementation guides to give others nationwide a manual of sorts for building and tweaking their own programs. The project culminated in an evaluation of the Kane County program’s first 13 months (summarized in the article above by RSI Director of Research Jennifer Shack), assessing program use, services provided, mediation outcomes and participant experience.
A Few Key Findings
The amount of information we have learned and done our best to share during the course of this project has been staggering. While any summation is sure to be incomplete, we’d like to leave you with a few key findings from the project:
- Integrated and holistic service delivery approaches truly made for better outcomes. Programs that took a comprehensive and progressive approach to combatting eviction saw more agreements and fewer evictions. Similarly, programs that brought more partners to the table, including social service agencies, advocacy groups, state and municipal representatives, and others, saw greater success. While eviction cases are ultimately resolved by courts, the underlying issues are economic and social in nature, and collaboration with entities that address those causes is highly valuable.
- Good eviction mediations take time. Prior to the pandemic, mediation in housing disputes, in many jurisdictions, was typically an event that took place on the day of the first court appearance and lasted no more than half an hour. Unsurprisingly, agreement rates in this context were generally low. A number of programs we worked with noted that utilizing a model where mediation was done outside of court (and the time constraints that usually entails) resulted in greater agreement. Allotting more time for the session gave greater opportunity to work through impasse, and scheduling mediation for an advance date gave parties the time to better prepare for mediation, including taking stock of finances, asking for support, applying for rental assistance, and consulting attorneys.
- Remote mediation, which is the norm for RSI’s programs and many others still, continues to offer mixed blessings for participants. The flexibility afforded parties by doing remote mediation meant many more parties could participate without taking a day off work, critical for parties trying desperately to pay back past due rent. On the other hand, our data noted that about 1 in 6 needed to borrow a device or leave home to participate virtually, and 1 in 5 experienced some sort of technical difficulty. Making sure that in-person accommodations could be offered to those who could not or would prefer not to participate virtually ought to be a priority to ensure access, and RSI did so with our Kane County program.
We are tremendously grateful to the AAA-ICDR Foundation for its support of this project.